The Bass model is most often used to forecast first time purchases of new-to-world products.
The model tries to capture the adoption rates of two types of users—innovators and imitators. Innovators are early adopters of new products and are driven by their desire to try new technology. Imitators are more wary of new technology—they tend to adopt only after receiving feedback from others.
The Bass model uses two coefficients to quantify the adoption rates. The Coefficient of Innovation, referred to in the literature as “p”, controls the adoption rate for the innovators. The Coefficient of Imitation, referred to in the literature as “q” controls the adoption rate for the imitators.
If you have 5 or more historic data points, these coefficients can be fit to the data. To build a Bass model with fewer than 5 data points you must set the values for these coefficients along with the total number of potential adopters. Typically, “p” is between 0 and 0.1, while “q” is between 0.3 and 0.5.
Clicking the Bass Diffusion icon or selecting Forecasting>New Products>Bass Diffusion on the Navigator context menu invokes the Bass Diffusion Model Settings dialog box shown below.
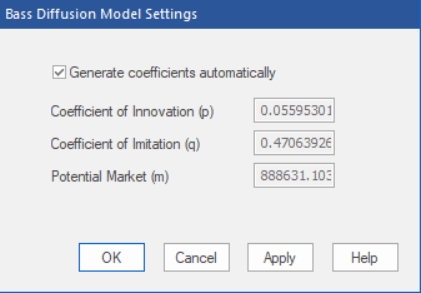
If you have five or more data points, the Generate coefficients automatically option allows you to instruct Forecast Pro to automatically fit the model parameters to the data. If you do not select Generate coefficients automatically, you’ll need to supply the model coefficients and potential market size.
The modifiers associated with the Bass diffusion model are:
\BASS. Use the Bass diffusion model with automatically generated coefficients and potential market size.
\BASS(p,q,m). Use the Bass diffusion model with user defined parameters p, q and m.